Shoulder
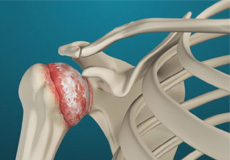
Arthritis of the Shoulder
The term arthritis literally means inflammation of a joint but is generally used to describe any condition in which there is damage to the cartilage. Damage of the cartilage in the shoulder joint causes shoulder arthritis. Inflammation is the body's natural response to injury. The warning signs that inflammation presents are redness, swelling, heat, and pain.
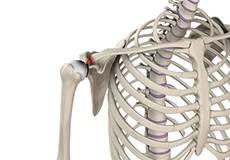
Acromioclavicular (AC) Arthritis
The acromioclavicular joint is part of the shoulder joint. It is formed by the union of the acromion, a bony process of the shoulder blade, and the outer end of the collar bone or clavicle. The joint is lined by cartilage that gradually wears with age as well as with repeated overhead or shoulder level activities such as basketball. The condition is referred to as AC arthritis or acromioclavicular arthritis.
Shoulder Pain
Pain in the shoulder may suggest an injury, which is more common in athletes participating in sports such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting. The injuries are caused due to the over usage or repetitive motion of the arms.
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff is a group of tendons in the shoulder joint that provides support and enables a wide range of motion. A major injury to these tendons may result in rotator cuff tears. It is one of the most common causes of shoulder pain in middle-aged and older individuals.
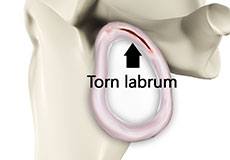
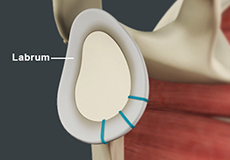
Shoulder Labral Tear
Traumatic injury to the shoulder or overuse of the shoulder (throwing, weightlifting) may cause the labrum to tear. In addition, aging may weaken the labrum leading to injury.
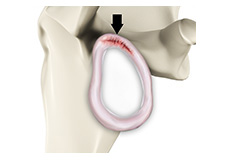
SLAP Tears
The term SLAP (superior–labrum anterior-posterior) lesion or SLAP tear refers to an injury of the superior labrum of the shoulder.
Rotator Cuff Pain
The rotator cuff consists of a group of tendons and muscles that surround and stabilize the shoulder joint. These tendons allow a wide range of movement of the shoulder joint across multiple planes. Irritation or injury to these tendons can result in rotator cuff pain.
Shoulder Instability
Shoulder instability is a chronic condition that causes frequent dislocation of the shoulder joint.
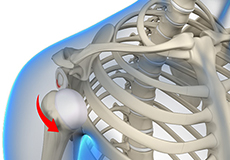
Shoulder Dislocation
Sports that involve overhead movements and repeated use of the shoulder at your workplace may lead to sliding of the upper arm bone from the glenoid. The dislocation might be a partial dislocation (subluxation) or a complete dislocation causing pain and shoulder joint instability.
Bicep Tendon Rupture
The biceps muscle is located in the front side of your upper arm and functions to help you bend and rotate your arm.
Shoulder Fracture
A break in the bone that makes up the shoulder joint is called a shoulder fracture. The clavicle (collarbone) and end of the humerus (upper arm bone) closest to the shoulder are the bones that usually are fractured. The scapula, or shoulder blade, is not easily fractured because of its protective cover of surrounding muscles and chest tissue.
Frozen Shoulder
Frozen shoulder, also called adhesive capsulitis, is a condition in which you experience pain and stiffness in your shoulder. The symptoms appear slowly, worsen gradually and usually take one to three years to resolve on their own.
Fracture of the Shoulder Blade (Scapula)
The scapula (shoulder blade) is a flat, triangular bone providing attachment to the muscles of the back, neck, chest and arm. The scapula has a body, neck and spine portion.
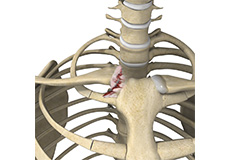
Clavicle Fracture
The break or fracture of the clavicle (collarbone) is a common sports injury associated with contact sports such as football and martial arts, as well as impact sports such as motor racing. A direct blow over the shoulder that may occur during a fall on an outstretched arm or a motor vehicle accident may cause the clavicle bone to break.
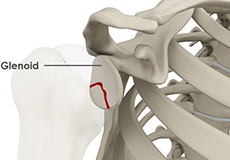
Glenoid Fractures
Fractures of the glenoid are rare but can occur due to major trauma or during high-energy sports activities.
Proximal Humerus Fractures
The humerus is the bone that forms the upper arm. It articulates with the glenoid cavity of the scapula (shoulder blade) to form the shoulder joint and with the lower arm bones – the ulna and radius – to form the elbow joint. The proximal humerus is the upper end of the arm bone that forms the shoulder joint.
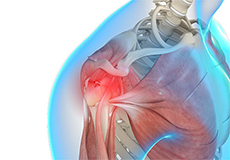
Subacromial Impingement Syndrome
SAIS is the inflammation and irritation of your rotator cuff tendons. This occurs when the tendons rub against the outer end of the shoulder blade (the acromion) while passing through the subacromial space during shoulder movement.
Anterior Shoulder Instability
Anterior shoulder instability, also known as anterior glenohumeral instability, is a condition in which damage to the soft tissues or bone causes the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) to dislocate or sublux from the glenoid fossa, compromising the function of the shoulder.
Posterior Shoulder Instability
Posterior shoulder instability, also known as posterior glenohumeral instability, is a condition in which the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) dislocates or subluxes posteriorly from the glenoid (socket portion of the shoulder) as a result of significant trauma. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation whereas a complete separation is referred to as a dislocation.
Overhead Athlete's Shoulder
An overhead athlete is at increased risk of injury due to the mechanism associated with rapid shoulder elevation, external rotation, and abduction. An overhead throwing motion is an intricate and skillful movement that presents a special challenge of needing the glenohumeral joint to surpass its physiologic limits during overhead sports activities.
Snapping Scapula
Snapping scapula or snapping scapula syndrome is also known as scapulothoracic syndrome or scapulocostal syndrome. It is a condition characterized by painful clicking, snapping, or grinding of the shoulder blade. The sound occurs as a result of rubbing of soft tissues between the thoracic wall and the scapula.
Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder impingement is the inflammation of the tendons of the shoulder joint. It is one of the most common causes of pain in the shoulder. Shoulder impingement is also called swimmer’s shoulder, tennis shoulder or rotator cuff tendinitis.
Shoulder Trauma
Shoulder injuries most commonly occur in athletes participating in sports such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting. The injuries are caused due to the over usage or repetitive motion of the arms.
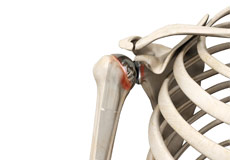
Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also called degenerative joint disease, is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs most often in older people. AC joint osteoarthritis affects the tissue covering the ends of bones (cartilage) in the AC joint of the shoulder. The cartilage becomes damaged and worn out causing pain, swelling, stiffness and restricted movement in the AC joint.
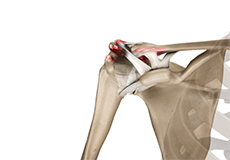
AC Joint Separation
AC joint separation, also known as shoulder separation, is a condition characterized by damage to the ligaments that connect the acromion to the collar bone. As a result, the bones do not line up properly, causing joint pain and instability.
Shoulder Tendonitis
Shoulder tendonitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the tendons which connect the muscles to the shoulder bones. Tendonitis of the rotator cuff tendons is known as rotator cuff tendonitis. If the biceps tendon is affected, the condition is known as bicipital tendonitis.
Throwing Injuries of the Shoulder
Throwing injuries of the shoulder are injuries sustained as a result of trauma by athletes during sports activities that involve repetitive overhand motions of the arm as in baseball, American football, volleyball, rugby, tennis, track and field events, etc.
Shoulder Disorders
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body that enables a wide range of movements. Aging, trauma or sports activities can cause injuries and disorders that can range from minor sprains or strains to severe shoulder trauma.
Baseball and Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries in baseball players are usually associated with pitching. While this overhand throwing activity can produce great speed and distance for the ball, when performed repeatedly, can place a lot of stress on the shoulder. While pitching, the arm is thrown outward and backward to generate speed.
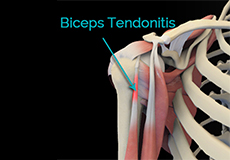
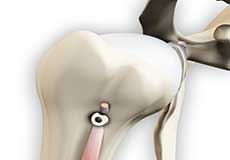
Proximal Biceps Tendinitis
Proximal biceps tendinitis is the irritation and inflammation of the biceps tendon at the shoulder joint. The biceps muscle is the muscle of the upper arm which is necessary for the movement of the shoulder and elbow.
Partial Rotator Cuff Tear
A partial rotator cuff tear is an incomplete tear that involves damage to a part of the tendon. The tear can be at the top, bottom or inner side of the tendon and does not go all the way through the tendon completely.
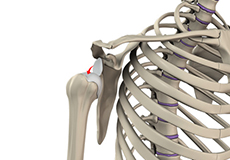
Shoulder Labral Tear with Instability
The shoulder consists of a ball-and-socket joint formed by the upper end of the humerus (upper arm bone) and a cavity in the shoulder blade called the glenoid. The glenoid cavity is surrounded by a rim of cartilage called the labrum. The labrum adds depth to the cavity making the joint more stable and positions the ball within the socket.
Proximal Biceps Tendon Rupture
The biceps muscle is the muscle of the upper arm which is necessary for the movement of the shoulder and elbow. It is made of a ‘short head’ and a ‘long head’ which function together. These are connected to the shoulder joint by two tendons called the proximal biceps tendons and to the elbow joint by a single distal biceps tendon.
Multidirectional Instability of the Shoulder
The shoulder consists of a ball and socket joint where the rounded end of the humerus (upper arm bone) fits into a socket (glenoid cavity) formed by the shoulder blade. The joint is stabilized by the surrounding capsule, ligaments, and tendons of the rotator cuff muscles.
AC Joint Dislocation/Acromioclavicular Joint Dislocation
A dislocation occurs when the ends of your bones are partially or completely moved out of their normal position in a joint. A partial dislocation is referred to as a subluxation, whereas a complete separation is referred to as a dislocation.
Internal Impingement of the Shoulder
Internal shoulder impingement can be described as a pathological condition resulting from repetitive impingement of the internal surface of the rotator cuff by the bones at the back of the glenohumeral joint.
Rotator Cuff Re-tear
Rotator cuff repair is a surgery to repair an injured or torn rotator cuff. A re-tear may occur a few years after surgery due to multiple reasons including aging, a massive previous tear (more than 5cm), fatty degradation of the tendons, inflammatory arthritis, and inappropriate rehabilitation.
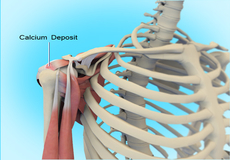
Calcification Tendinitis
Calcification tendinitis is a problem with the shoulder’s tendons and muscles. This condition occurs due to the formation of calcium deposits in the tendons (tissue which attaches muscle to bone) of the rotator cuff (a group of muscles and tendons stabilizing the shoulder).
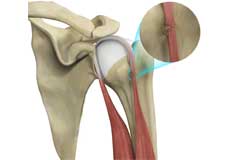
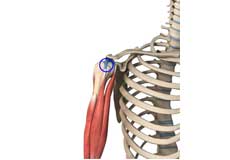
Long Head Biceps Tendon Rupture
Your biceps muscle has two heads, a long head, and a short head, which are both attached to the shoulder. The long head of the biceps tendon is a tough band of connective fibrous tissue that attaches the long head of the biceps to the top of the shoulder socket.
Massive Retracted Rotator Cuff Tear
A tear in the rotator cuff can cause pain and disability. It can occur from degeneration of the rotator cuff due to overuse or from a sudden injury. Massive rotator cuff tears involve tears in two complete tendons of the rotator cuff. A tear of more than 5 cm is described as massive.
Periprosthetic Shoulder Fracture
A periprosthetic shoulder fracture is a fracture that occurs in the bone adjacent to a shoulder prosthesis.
Shoulder Joint Replacement
Total shoulder replacement surgery is performed to relieve symptoms of severe shoulder pain and disability due to arthritis. In this surgery, the damaged articulating parts of the shoulder joint are removed and replaced with artificial prostheses. Replacement of both the humeral head and the socket is called a total shoulder replacement.
Minimally Invasive Shoulder Joint Replacement
Shoulder joint replacement is a surgical procedure that replaces damaged bone surfaces with artificial humeral and glenoid components to relieve pain and improve functional ability in the shoulder joint.
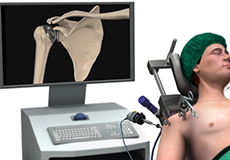
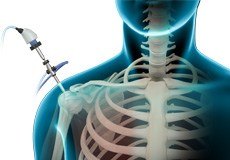
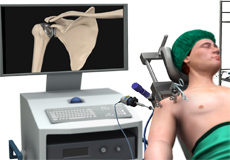
Shoulder Arthroscopy
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and surgical procedure performed for joint problems. Shoulder arthroscopy is performed using a pencil-sized instrument called an arthroscope. The arthroscope consists of a light system and camera that projects images of the surgical site onto a computer screen for your surgeon to clearly view.
Rotator Cuff Repair
Rotator cuff repair is a surgery to repair an injured or torn rotator cuff. It is usually performed arthroscopically on an outpatient basis. An arthroscope, a small, fiber-optic instrument consisting of a lens, light source, and video camera. The camera projects images of the inside of the joint onto a large monitor, allowing your doctor to look for any damage, assess the type of injury and repair it. Large rotator cuff tears may require open surgery.
SLAP Repair
A SLAP repair is an arthroscopic shoulder procedure to treat a specific type of injury to the labrum called a SLAP tear.
Revision Shoulder Replacement
Revision surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia. You are positioned in such a way as to allow all possible variations in the treatment plan. Incisions are made to gain optimal access to the problem and usually follow previous incisions with extensions made as necessary.
Reverse Shoulder Replacement
Conventional surgical methods such as total shoulder joint replacement are not very effective in the treatment of rotator cuff arthropathy. Reverse total shoulder replacement is an advanced surgical technique specifically designed for rotator cuff tear arthropathy, a condition where you suffer from both shoulder arthritis and a rotator cuff tear.
Shoulder Preservation Surgery
Shoulder preservation surgery is any surgical procedure that is aimed at preserving the structure and function of the shoulder. It may be a good option when non-surgical treatments fail to relieve shoulder symptoms as it is less invasive than shoulder joint replacement surgery.
Shoulder Resurfacing
The shoulder is an active joint is prone to injuries and may also get affected by conditions such as arthritis, which results in impaired functioning and related discomfort. The traditional method of treatment for such conditions is shoulder joint replacement. However, advances in technology have resulted in a superior alternative technique known as shoulder resurfacing.
Proximal Biceps Tenodesis
Proximal biceps tenodesis is the surgical reattachment of a torn proximal biceps tendon, which connects the upper part of your biceps muscle to the shoulder.
Sternoclavicular Joint Reconstruction
Sternoclavicular joint reconstruction is a surgical procedure employed to repair and restore full function of a damaged sternoclavicular joint.
AC Joint Stabilisation
Acromioclavicular (AC) joint stabilization is a surgical procedure employed to treat severe cases of AC joint dislocation.
SC Joint Injury Reconstruction
The sternoclavicular (SC) joint is the joint between the breastbone (sternum) and the collar bone (clavicle). Injuries to this joint are called sternoclavicular joint injuries and can include stretching or tearing of the ligaments. It is usually caused due to severe trauma or a direct blow to the side of your body such as in motor vehicle accidents or contact sports.
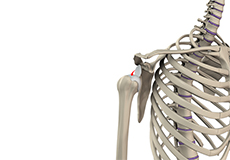
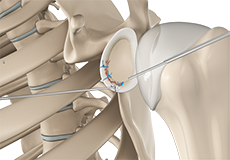
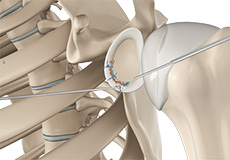
Arthroscopic Bankart Repair
The labrum can sometimes tear during a shoulder injury. A specific type of labral tear that occurs when the shoulder dislocates is called a Bankart tear. This is a tear to a part of the labrum called the inferior glenohumeral ligament and is common in the young who sustain a dislocation of the shoulder.
Shoulder Labrum Reconstruction
Traumatic injury to the shoulder or overuse of the shoulder by excessive throwing or weightlifting can cause a labral tear. In addition, the aging process may weaken the labrum, leading to injury secondary to wear and tear.
Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Reconstruction
The acromioclavicular (AC) joint is one of the joints present within your shoulder. It is formed between a bony projection at the top of the shoulder blade (acromion) and the outer end of the clavicle (collarbone). The joint is enclosed by a capsule and supported by ligaments.
Shoulder Fracture Care
A break in the bone that makes up the shoulder joint is called a shoulder fracture. The clavicle (collarbone) and end of the humerus (upper arm bone) closest to the shoulder are the bones that usually are fractured. The scapula, or shoulder blade, is not easily fractured because of its protective cover of surrounding muscles and chest tissue.
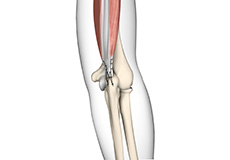
Triceps Repair
Triceps repair is a surgical procedure that involves the repair of a ruptured (torn) triceps tendon. A tendon is a tough band of fibrous tissue which connects muscle to bone and works together with muscles in moving your arms, fingers, legs, and toes. The triceps tendons connect the triceps muscles to the shoulder blade and elbow in your arm.
Arthroscopic Frozen Shoulder Release
An arthroscopic frozen shoulder release is a minimally-invasive shoulder surgery performed to relieve pain and restore normal function using a special instrument called an “arthroscope”.
Distal Clavicle Excision
Distal clavicle excision is a procedure which involves removal of the outer end of the clavicle (collarbone) to treat shoulder pain and disability due to arthritis or impingement.
Bony Instability Reconstruction of the Shoulder
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body. Injury and trauma can tear or stretch the labrum and/or ligaments, causing loosening and instability of the shoulder joint which can lead to partial or complete dislocation of the joint.
Non-surgical Shoulder Treatments
Rest plays an important role in restoring shoulder health and shouldn’t be taken lightly. Usually, a sling is worn to keep the arm immobile and stable. You should try to avoid using the injured arm as straining the injured shoulder may lead to future complications. Physical rest can also help keep inflammation under control.
 The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body that enables a wide range of movements including forward flexion, abduction, adduction, external rotation, internal rotation, and 360-degree circumduction. Thus, the shoulder joint is considered the most insecure joint of the body, but the support of ligaments, muscles, and tendons function to provide the required stability.
The shoulder is the most flexible joint in the body that enables a wide range of movements including forward flexion, abduction, adduction, external rotation, internal rotation, and 360-degree circumduction. Thus, the shoulder joint is considered the most insecure joint of the body, but the support of ligaments, muscles, and tendons function to provide the required stability.
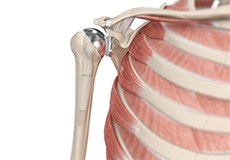
Bones of the Shoulder
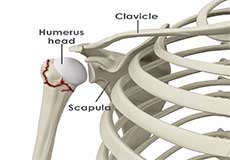
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint made up of three bones, namely the humerus, scapula, and clavicle.
Humerus
The end of the humerus or upper arm bone forms the ball of the shoulder joint. An irregular shallow cavity in the scapula called the glenoid cavity forms the socket for the head of the humerus to fit in. The two bones together form the glenohumeral joint, which is the main joint of the shoulder.
Scapula and Clavicle
The scapula is a flat triangular-shaped bone that forms the shoulder blade. It serves as the site of attachment for most of the muscles that provide movement and stability to the joint. The scapula has four bony processes - acromion, spine, coracoid and glenoid cavity. The acromion and coracoid process serve as places for attachment of the ligaments and tendons.
The clavicle bone or collarbone is an S-shaped bone that connects the scapula to the sternum or breastbone. It forms two joints: the acromioclavicular joint, where it articulates with the acromion process of the scapula and the sternoclavicular joint where it articulates with the sternum or breast bone. The clavicle also forms a protective covering for important nerves and blood vessels that pass under it from the spine to the arms.
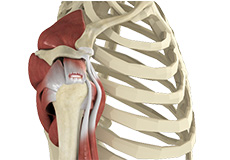
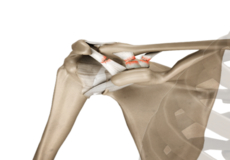
Soft Tissues of the Shoulder
The ends of all articulating bones are covered by smooth tissue called articular cartilage, which allows the bones to slide over each other without friction, enabling smooth movement. Articular cartilage reduces pressure and acts as a shock absorber during movement of the shoulder bones. Extra stability to the glenohumeral joint is provided by the glenoid labrum, a ring of fibrous cartilage that surrounds the glenoid cavity. The glenoid labrum increases the depth and surface area of the glenoid cavity to provide a more secure fit for the half-spherical head of the humerus.
Ligaments of the Shoulder
Ligaments are thick strands of fibers that connect one bone to another. The ligaments of the shoulder joint include:
- Coracoclavicular ligaments: These ligaments connect the collarbone to the shoulder blade at the coracoid process.
- Acromioclavicular ligament: This connects the collarbone to the shoulder blade at the acromion process.
- Coracoacromial ligament: It connects the acromion process to the coracoid process.
- Glenohumeral ligaments: A group of 3 ligaments that form a capsule around the shoulder joint and connect the head of the arm bone to the glenoid cavity of the shoulder blade. The capsule forms a watertight sac around the joint. Glenohumeral ligaments play a very important role in providing stability to the otherwise unstable shoulder joint by preventing dislocation.
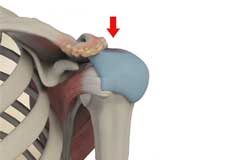
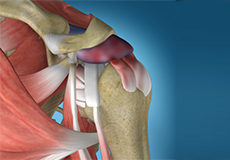
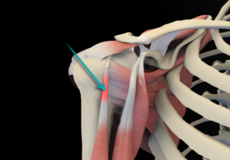
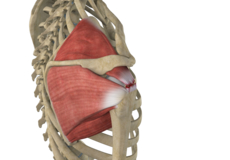
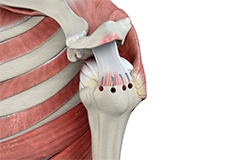
Muscles of the Shoulder
The rotator cuff is the main group of muscles in the shoulder joint and is comprised of 4 muscles. The rotator cuff forms a sleeve around the humeral head and glenoid cavity, providing additional stability to the shoulder joint while enabling a wide range of mobility. The deltoid muscle forms the outer layer of the rotator cuff and is the largest and strongest muscle of the shoulder joint.
Tendons of the Shoulder
Tendons are strong tissues that join muscle to bone allowing the muscle to control the movement of the bone or joint. Two important groups of tendons in the shoulder joint are the biceps tendons and rotator cuff tendons.
Bicep tendons are the two tendons that join the bicep muscle of the upper arm to the shoulder. They are referred to as the long head and short head of the bicep.
Rotator cuff tendons are a group of four tendons that join the head of the humerus to the deeper muscles of the rotator cuff. These tendons provide more stability and mobility to the shoulder joint.
Nerves of the Shoulder
Nerves carry messages from the brain to muscles to direct movement (motor nerves) and send information about different sensations such as touch, temperature, and pain from the muscles back to the brain (sensory nerves). The nerves of the arm pass through the shoulder joint from the neck. These nerves form a bundle at the region of the shoulder called the brachial plexus. The main nerves of the brachial plexus are the musculocutaneous, axillary, radial, ulnar and median nerves.
Blood vessels of the Shoulder
Blood vessels travel along with the nerves to supply blood to the arms. Oxygenated blood is supplied to the shoulder region by the subclavian artery that runs below the collarbone. As it enters the region of the armpit, it is called the axillary artery and further down the arm, it is called the brachial artery.
The main veins carrying de-oxygenated blood back to the heart for purification include:
- Axillary vein: This vein drains into the subclavian vein.
- Cephalic vein: This vein is found in the upper arm and branches at the elbow into the forearm region. It drains into the axillary vein.
- Basilic vein: This vein runs opposite the cephalic vein, near the triceps muscle. It drains into the axillary vein.